Introduction
Understanding the layers beneath a lawn is essential for maintaining a healthy and vibrant outdoor space. These layers, including topsoil and subsoil, are crucial for nutrient absorption, moisture retention, and overall grass vitality. Unfortunately, many homeowners overlook these foundational elements, which can lead to issues such as poor drainage and nutrient deficiencies.
What insights do these hidden layers provide, and how can they elevate an ordinary lawn into a lush oasis?
Defining Lawn Layers: What Lies Beneath Grass
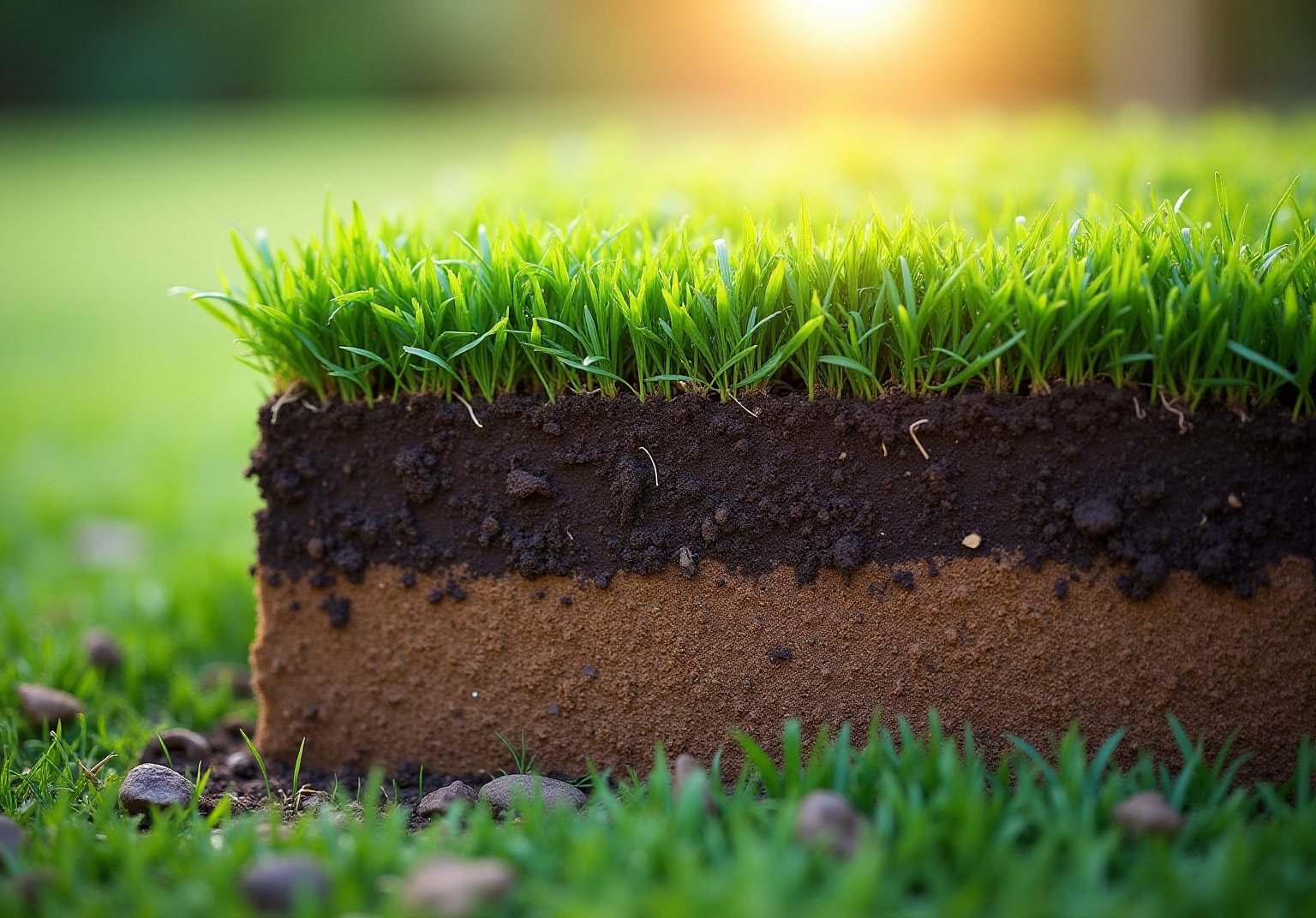
Lawn strata refer to what is under grass, encompassing the distinct levels of materials and soil beneath the turf surface, each playing a critical role in the overall health and functionality of the lawn. The primary components include:
- Topsoil
- Subsoil
- Occasionally a layer of organic matter or mulch
Topsoil, the uppermost stratum, is rich in nutrients and organic matter, providing the essential environment for turf roots to flourish. Beneath it lies the subsoil, which is denser and less fertile but still important for drainage and root expansion.
Understanding these layers is essential for effective yard maintenance, as they influence water retention, nutrient availability, and overall plant vitality. Research indicates that healthy topsoil can significantly enhance a turf’s capacity to retain moisture and nutrients, which is crucial for maintaining plant health. Alarmingly, over the past 40 years, we have lost 40% of our topsoil, underscoring the urgent need for its preservation. Furthermore, the subsoil contributes to the turf’s resilience against drought and encourages deeper rooting, enabling grass to access water and nutrients more effectively.
Effective garden care initiatives often focus on managing these strata, ensuring that topsoil is enriched with organic matter and that subsoil is aerated to improve drainage. As Jon Trappe, a turfgrass educator, notes, “Lawns have a place in society based on how we want to use them,” highlighting their functional and cultural significance. By prioritizing the health of both topsoil and subsoil, homeowners can cultivate vibrant, lush lawns that not only enhance their outdoor spaces but also contribute positively to the environment, improving air quality and reducing noise levels.
Understanding the Importance of Lawn Layers for Grass Health
What is under grass, namely the strata beneath vegetation, plays a crucial role for several reasons. They provide essential nutrients and moisture necessary for turf to thrive. A healthy topsoil layer, rich in organic matter, fosters microbial life that breaks down nutrients, making them accessible to grass roots. Additionally, the arrangement of these strata significantly influences water drainage and retention. Well-aerated soil enhances water infiltration, reducing runoff and promoting deeper root growth. Understanding what is under grass is crucial for diagnosing grass issues, such as poor drainage or nutrient deficiencies, which enables targeted interventions for grass improvement.
The Evolution of Lawn Layers: Historical Context and Development
The evolution of grass layers signifies a major transformation in landscaping practices throughout history. Initially, green spaces served as basic areas for grazing or decorative purposes. However, as landscaping techniques advanced, particularly during the 18th and 19th centuries, a deeper understanding of what is under grass and soil composition emerged, highlighting its crucial role in turf health.
The introduction of fertilizers and soil enhancers marked a pivotal shift in grass care, allowing for the cultivation of lush, manicured lawns that became symbols of status and beauty. As Brooks Pennington Jr., founder of Pennington Seed, noted, “The emphasis on grass seed for yards and turf has changed our approach to landscaping, highlighting the significance of quality and attention.”
Today, modern landscaping emphasizes sustainable practices that prioritize organic matter and the health of soil ecosystems. This contemporary approach not only enhances the visual appeal of green spaces but also fosters environmental stewardship.
The historical development of turf maintenance underscores the intrinsic link between soil health and the aesthetic quality of landscapes, illustrating that what is under grass is essential for a vibrant landscape rooted in well-managed soil.
Key Characteristics of Lawn Layers: Composition and Function
The essential traits of turf sections, including their unique composition, structure, and function, are crucial for understanding what is under grass and how it impacts plant health. The topsoil layer, enriched with a mix of sand, silt, clay, and organic matter, creates a fertile environment that is crucial for nutrient absorption and moisture retention. This layer is fundamental for fostering robust grass growth.
What is under grass consists of the subsoil, which, although denser and typically lower in nutrients, is essential for effective drainage and providing structural support for roots. Incorporating organic materials, such as compost or mulch, significantly enhances soil health by improving moisture retention and encouraging beneficial microbial activity.
Research indicates that well-structured grass layers can retain moisture more effectively, with organic-rich soils demonstrating superior capabilities compared to those with minimal organic content. For example, studies have shown that soils with higher organic matter can retain up to 20% more moisture than those with lower levels.
By understanding these characteristics, homeowners and landscapers can adopt informed care practices that promote optimal plant health and longevity. As farmer Ron Juris emphasizes, “Maximizing water retention is key to maintaining healthy grass, especially in dry seasons.” This insight highlights the importance of effectively managing lawn layers.
Conclusion
Understanding the layers beneath grass is crucial for maintaining a healthy lawn. These layers, primarily topsoil and subsoil, play essential roles in nutrient retention, moisture management, and overall plant vitality. Recognizing the significance of these strata not only aids in effective yard maintenance but also highlights the urgent need to preserve topsoil, which has faced alarming declines in recent decades.
Key insights regarding the composition and functions of lawn layers have been shared:
- Topsoil, enriched with organic matter, fosters a thriving ecosystem for grass roots.
- Subsoil supports drainage and root expansion.
Historical context illustrates the evolution of lawn care practices, emphasizing a shift towards sustainable landscaping that prioritizes soil health. The characteristics of these layers, including their ability to retain moisture and nutrients, underscore the necessity for informed care practices that promote robust grass growth.
Ultimately, the health of a lawn is intricately linked to the layers beneath its surface. By prioritizing the management of topsoil and subsoil, homeowners can cultivate not only beautiful outdoor spaces but also contribute positively to the environment. Embracing sustainable practices in lawn care is a crucial step toward ensuring vibrant landscapes that benefit both people and nature.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are lawn strata?
Lawn strata refer to the distinct layers of materials and soil beneath the grass, which include topsoil, subsoil, and sometimes a layer of organic matter or mulch.
What is the role of topsoil in lawn health?
Topsoil is the uppermost layer rich in nutrients and organic matter, providing an essential environment for turf roots to flourish.
How does subsoil contribute to lawn health?
Subsoil lies beneath topsoil and is denser and less fertile, but it plays a crucial role in drainage and root expansion, contributing to the lawn’s resilience against drought.
Why is understanding lawn layers important for yard maintenance?
Understanding lawn layers is essential because they influence water retention, nutrient availability, and overall plant vitality, which are critical for maintaining a healthy lawn.
What has happened to topsoil over the past 40 years?
Over the past 40 years, we have lost 40% of our topsoil, highlighting the urgent need for its preservation.
How can homeowners improve the health of their lawns?
Homeowners can improve lawn health by enriching topsoil with organic matter and aerating subsoil to enhance drainage.
What cultural significance do lawns have according to turfgrass educators?
Lawns have a place in society based on how we want to use them, indicating their functional and cultural significance.
How do healthy lawns contribute to the environment?
Healthy lawns can enhance outdoor spaces, improve air quality, and reduce noise levels, contributing positively to the environment.

