Introduction
The emergence of artificial turf has significantly altered the landscaping options available to homeowners, presenting an appealing solution for those in search of low-maintenance and visually attractive outdoor spaces.
However, underlying this convenience are complex environmental issues that warrant thorough examination.
As the consequences of synthetic grass become more evident, homeowners face the challenge of reconciling the benefits of ease with potential ecological impacts.
This article investigates the diverse environmental effects of artificial turf, weighing its advantages against its disadvantages, and aims to guide property owners toward informed choices that support sustainable practices.
Explore the Basics of Artificial Turf and Its Environmental Concerns
Artificial surfaces made from synthetic fibers that mimic natural grass have gained popularity due to their low maintenance and aesthetic appeal. However, they pose significant environmental challenges:
-
Material Composition: Primarily constructed from petroleum-based plastics, artificial turf contributes to fossil fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions during production. This dependence on non-renewable resources raises sustainability concerns related to the artificial turf environmental impact.
-
Artificial turf environmental impact: The deterioration of synthetic grass leads to the release of microplastics into the environment. Studies indicate that these fibers can account for over 15% of plastic waste in aquatic ecosystems. Remarkably, up to 20,000 fibers can flow daily through rivers, contaminating soil and waterways and posing risks to wildlife.
-
Chemical Runoff: The infill materials used in synthetic grass often leach harmful substances, including heavy metals and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), into the surrounding ecosystem. This chemical runoff can adversely affect soil health and water quality, raising concerns for homeowners and local communities regarding the artificial turf environmental impact.
-
Heat Retention: Synthetic grass absorbs and retains heat, leading to surface temperatures that can exceed 120-160°F on sunny days. A study by Brigham Young University found that when air temperatures reach 98 degrees Fahrenheit, plastic field surfaces can surpass 200 degrees. This phenomenon contributes to the urban heat island effect, exacerbating local climate issues and increasing the risk of heat-related illnesses, particularly for children and athletes.
Understanding the artificial turf environmental impact is crucial for property owners who are considering synthetic grass as a landscaping option, particularly in light of growing initiatives that promote sustainable practices and alternatives.
Identify the Environmental Benefits of Artificial Turf for Homeowners
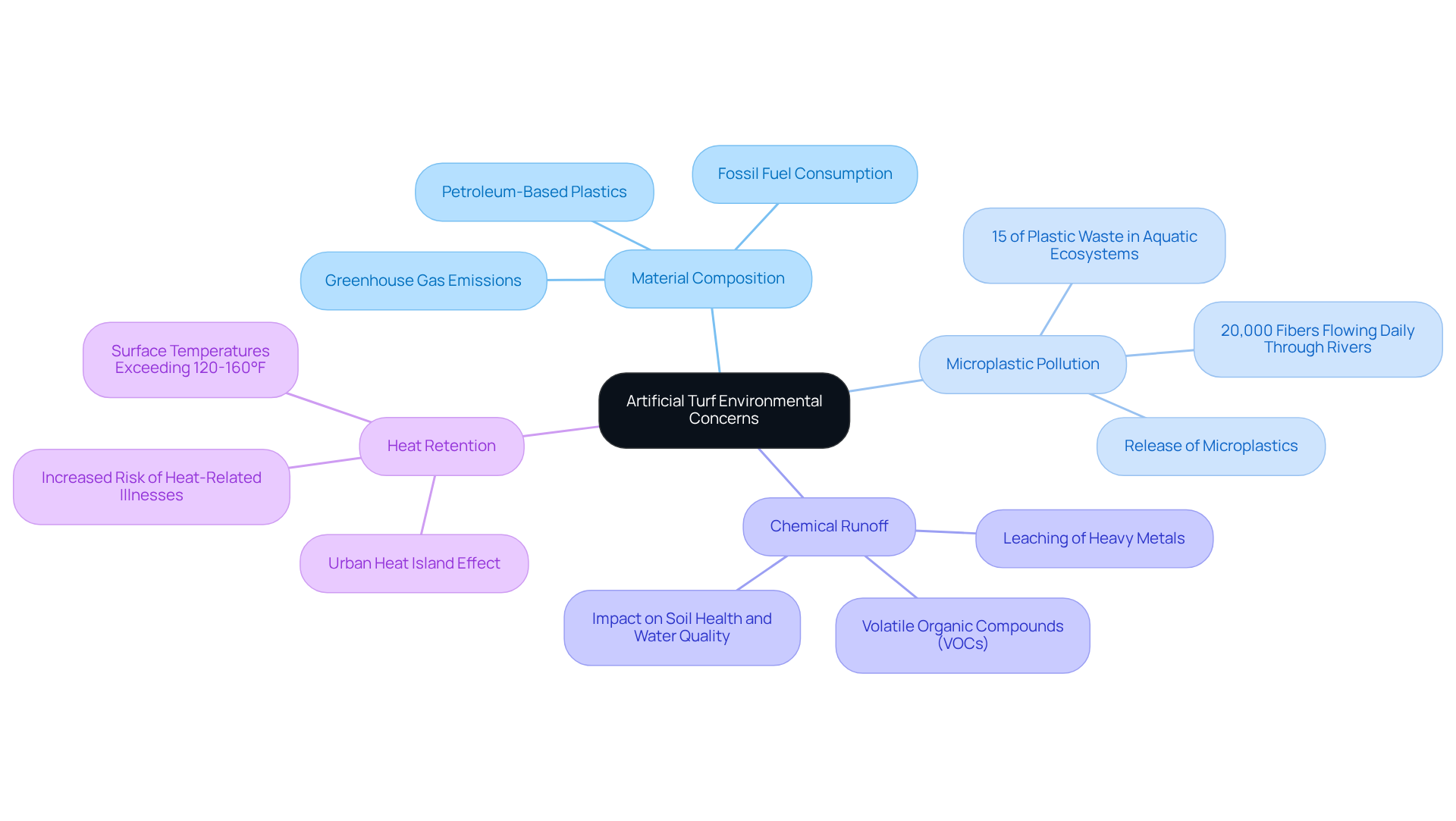
Artificial turf offers several environmental benefits that appeal to homeowners interested in sustainable landscaping options.
-
Water Conservation: A key advantage of artificial turf is its capacity to conserve water. Unlike natural sod, which can require up to 299,040 gallons annually for a standard 10,000 square foot lawn, artificial surfaces eliminate the need for watering. This conservation is particularly beneficial in drought-prone areas. In fact, synthetic surfaces use 70% less water than natural vegetation, enabling households to reduce their water consumption by 30-60% when transitioning to synthetic lawns.
-
Reduced Chemical Use: By opting for synthetic grass, homeowners can significantly lessen their dependence on harmful chemicals. Synthetic grass does not necessitate fertilizers, pesticides, or herbicides, which can pollute local ecosystems. This chemical-free maintenance approach not only protects the environment but also creates a safer play area for children and pets.
-
Lower Carbon Emissions: Transitioning to synthetic grass can lead to a reduction in carbon emissions. By decreasing the need for gas-powered lawn maintenance equipment, such as mowers and trimmers, homeowners help lower overall emissions, fostering a healthier environment.
-
Durability and Longevity: High-quality synthetic grass is designed to last, often exceeding 10 years with proper maintenance. This durability reduces the frequency of replacements, thereby minimizing waste and resource consumption associated with traditional lawn care.
-
Biodiversity Preservation: Choosing synthetic grass can aid in protecting natural environments that might otherwise be disrupted by conventional lawn care methods. By reducing the need for extensive landscaping, property owners can contribute to the preservation of local biodiversity.
While these compelling advantages make synthetic grass an attractive option for environmentally conscious homeowners, it is also essential to consider the artificial turf environmental impact associated with its production and disposal. Understanding the artificial turf environmental impact is vital for balancing the benefits of water conservation with potential environmental concerns.
Examine the Controversies and Drawbacks of Artificial Turf
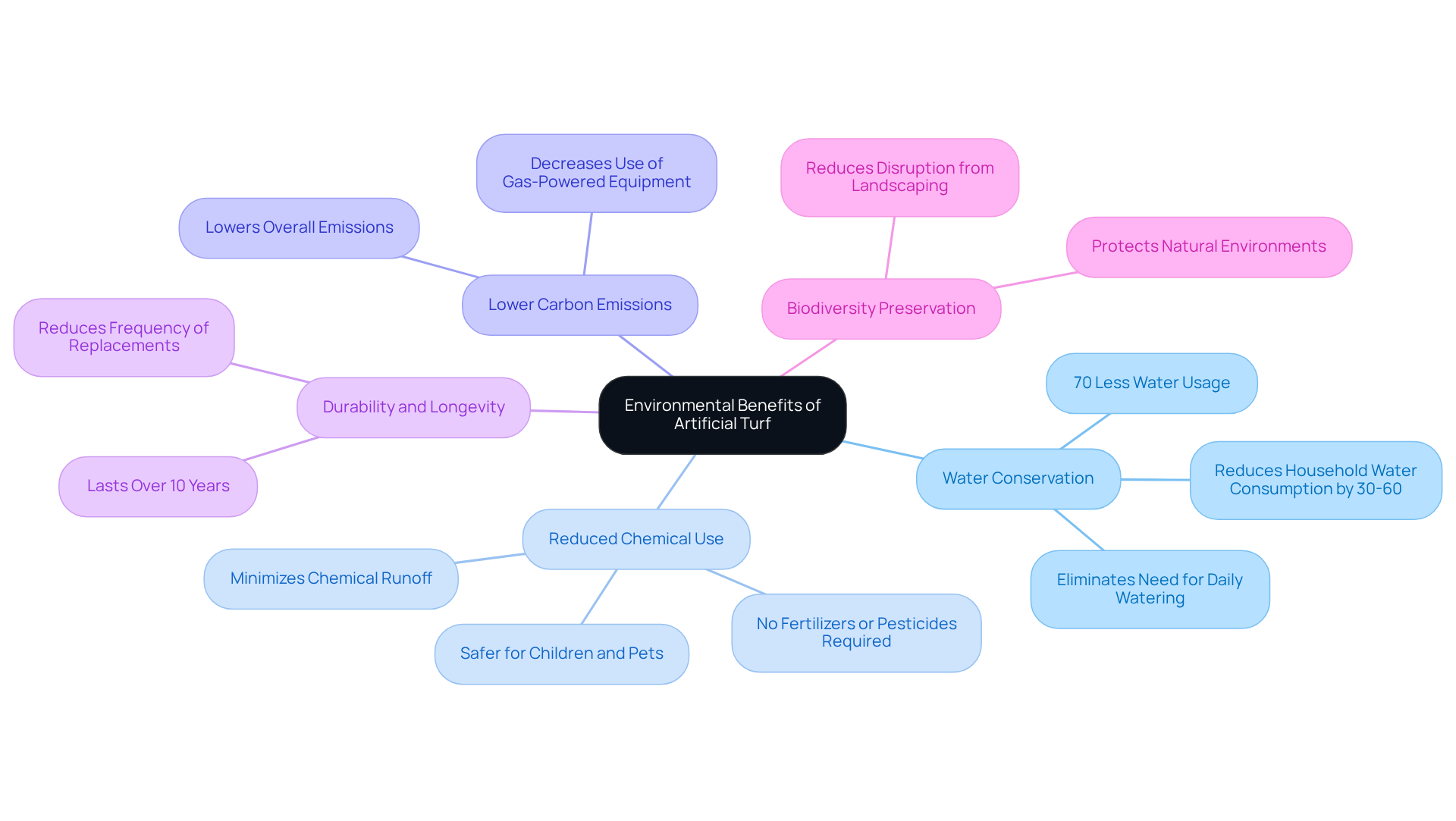
While artificial turf offers certain advantages, it is essential to consider several controversies and drawbacks:
-
Health Risks: There are significant concerns regarding harmful chemicals found in artificial turf, such as lead and phthalates. These substances can pose health risks to both children and pets.
-
The artificial turf environmental impact arises from the pollution and waste associated with its production and disposal. Many of these materials end up in landfills, where they may take centuries to decompose.
-
Heat Issues: Synthetic surfaces can reach temperatures significantly higher than natural grass, creating unsafe conditions for play. This heat absorption can also lead to increased energy costs for nearby buildings.
-
Microplastic Contamination: The degradation of synthetic grass can release microplastics into the environment, leading to widespread pollution that adversely affects wildlife and ecosystems.
-
Aesthetic Constraints: Some property owners may find that synthetic grass does not replicate the authentic appearance and texture of real grass, potentially impacting property value and curb appeal.
These disadvantages highlight the importance of careful evaluation of the artificial turf environmental impact before choosing synthetic grass.
Consider Practical Factors When Choosing Artificial Turf
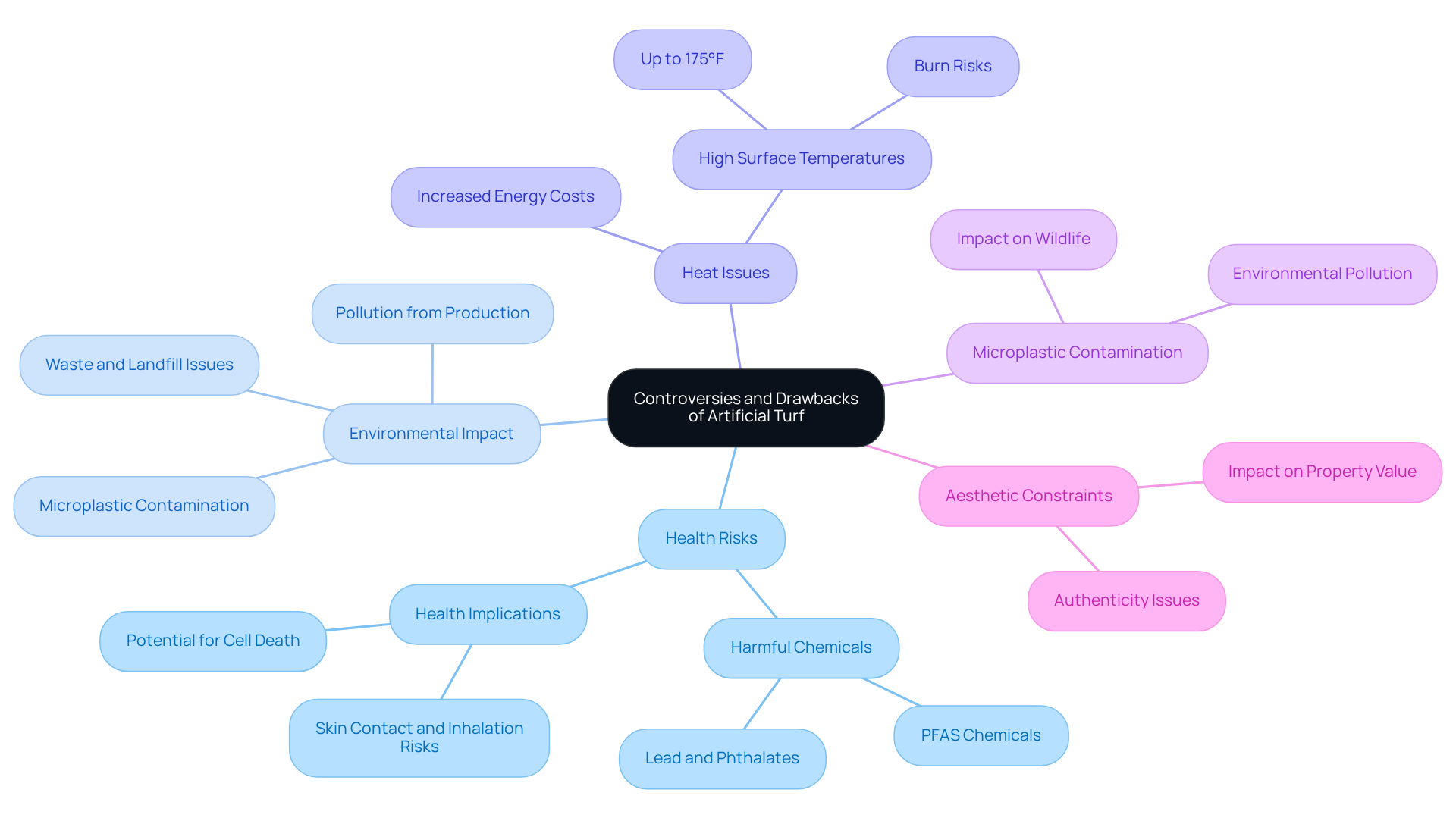
When selecting artificial turf, homeowners should consider several practical factors to ensure they make the best choice for their needs.
-
Intended Use: Identify the primary purpose of the turf-whether for play areas, landscaping, or sports-to select the appropriate type and quality. For instance, grass designed for high foot traffic areas, such as sports fields, is engineered for durability and performance.
-
Foot Traffic Durability: Assess the expected foot traffic to choose a product that can withstand wear and tear. Statistics indicate that synthetic grass can last between 8 to 15 years, depending on usage and maintenance levels. In high-traffic environments, surfaces engineered for durability are essential to prevent premature wear.
-
Climate Considerations: Take into account local climate conditions, as certain grass varieties perform better in specific environments. For example, polyethylene grass is known for its UV resistance, making it suitable for warmer climates where heat retention can be a concern.
-
Maintenance Requirements: Assess the maintenance needs of various grass options, including cleaning and infill replacement. Selecting low-maintenance grass can better suit a hectic lifestyle, minimizing the time and effort needed for upkeep.
Investigate the substances utilized in the grass and their artificial turf environmental impact. Choose items that emphasize sustainability and recyclability, as the artificial turf environmental impact is becoming a rising issue. Innovations in turf technology are addressing these concerns, with some products designed to minimize harmful emissions and enhance recyclability.
By considering these factors, homeowners can make informed choices that not only enhance their outdoor spaces but also contribute to a more sustainable environment.
Conclusion
The environmental impact of artificial turf presents a complex landscape for homeowners considering this landscaping option. While synthetic grass offers appealing benefits such as water conservation and reduced chemical usage, it also raises significant concerns regarding its production, disposal, and ecological footprint. Understanding these dual facets is essential for making informed decisions that align with sustainable practices.
Key insights highlight the balance between the advantages and drawbacks of artificial turf. Homeowners can enjoy lower water bills and a decrease in harmful chemical use, contributing to a safer environment. However, issues such as microplastic contamination, heat retention, and potential health risks cannot be overlooked. These factors underscore the importance of thorough research and consideration before opting for artificial surfaces.
Ultimately, the choice of artificial turf should reflect a commitment to environmental stewardship. Homeowners are encouraged to weigh the benefits against the potential negative impacts and consider innovations in turf technology that prioritize sustainability. By making informed choices, property owners can enhance their outdoor spaces while contributing positively to the environment, ensuring that their landscaping decisions support a healthier planet for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is artificial turf made of?
Artificial turf is primarily constructed from petroleum-based plastics.
What are the environmental concerns associated with artificial turf?
Environmental concerns include fossil fuel consumption during production, the release of microplastics into ecosystems, chemical runoff from infill materials, and heat retention that contributes to the urban heat island effect.
How does artificial turf contribute to plastic waste?
The deterioration of synthetic grass releases microplastics, which can account for over 15% of plastic waste in aquatic ecosystems, with up to 20,000 fibers flowing daily through rivers and contaminating soil and waterways.
What harmful substances can leach from artificial turf infill materials?
Infill materials can leach heavy metals and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the surrounding ecosystem, adversely affecting soil health and water quality.
What are the temperature concerns related to synthetic grass?
Synthetic grass can absorb and retain heat, leading to surface temperatures exceeding 120-160°F on sunny days, and can surpass 200 degrees when air temperatures reach 98°F, contributing to the urban heat island effect.
Why is it important to understand the environmental impact of artificial turf?
Understanding the environmental impact is crucial for property owners considering synthetic grass, especially in the context of growing initiatives that promote sustainable practices and alternatives.

